Diabetes has a long-term effect on the health of persons who have it, resulting in nerve damage, vision loss, and kidney disease, among other complications. However, it also affects a part of your wellbeing that is rarely discussed: your reproductive health.
Dr. Hrishikesh Pai, a well-known infertility specialist in Delhi, says that unchecked diabetes can impair the reproductive and fertility health of both women and men. It is linked to hormonal issues, low sperm quality, and DNA damage, which can cause irregular or interrupted menstrual periods in women and make it difficult for men to get and maintain erections.
How can diabetes affect your fertility?
Studies have shown that diabetes can affect your capacity to conceive and deliver a healthy baby. Diabetes influences both men’s and women’s fertility and reproductive health.
According to IDF (International Diabetes Federation), diabetes had affected more than 537 million adults worldwide by 2021, with about half of them having no idea they have it.
In terms of impacting fertility, diabetes can have varied effects on men and women.
What effect does diabetes have on female fertility?
Genitourinary infections: If you have diabetes, you are more prone to infections and damages to your reproductive organs, particularly the fallopian tubes.
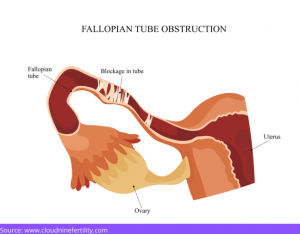
Pregnancy complications: High blood glucose (hyperglycemia) during pregnancy might lead to miscarriage or congenital abnormalities in your growing fetus. Macrosomia, also known as a big-baby syndrome, is caused by high blood glucose levels and excess nutrition for the developing fetus.

Reduced libido: You may experience reduced sexual desire due to anxiety, depression, and fatigue. Absent or reduced sexual desire will cause zero or minimal vaginal lubrication, which can result in discomfort and pain during sex.

Effect of type 1 diabetes in female fertility
Delayed menarche: Menarche is the first time a girl gets her periods. Type 1 diabetes in juveniles causes delayed or late menarche.
Menstrual cycle disturbances: Type 1 diabetes is linked to a longer menstrual cycle (more than 31 days), prolonged menstruation (6 days or more), heavier menstruation (excessive bleeding), and menstrual disorders at a younger age (less than 29 years).
Anovulation: Anovulation is the lack of ovulation in females post-menarche and pre-menopause. Anovulation can be caused by several things, including severe mental illness, hormonal imbalances, ovarian dysfunction, pituitary failure, and diabetes.
Diabetic women with a low BMI (Body Mass Index) will have menstrual irregularities, resulting in intracellular starvation (cell starvation) and leading to anovulation.
Anti-sperm antibodies: Antibodies produced by diabetes have the potential to harm sperm and your eggs.
Effect of type 2 diabetes in female fertility
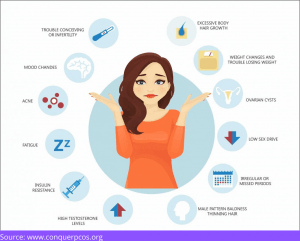
PCOS (Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome): Type 2 diabetes, which used to be more common in post-menopausal women previously, has been increasingly affecting women in their reproductive years. This is because obesity is on the rise due to modern food and lifestyle habits, increasing the risk of Type 2 diabetes in pre-menopausal women.
Obesity is connected to PCOS as well as menstrual irregularities. PCOS causes an overabundance of male hormones (androgens), irregular menstrual cycles/ anovulation, and cysts on the ovaries. Insulin resistance is present in 50-70 percent of women with PCOS.
What effect does diabetes have on male fertility?
Sexual dysfunction: Diabetes impairs men’s ability to sustain an erection, thus resulting in infertility.

Reduced libido: The functions of your brain, such as learning, thinking, and memory, are strongly linked to your glucose levels (the brain’s primary source of energy) and how effectively the brain uses this fuel source.

Dr. Hrishikesh Pai, a founder of Bloom IVF Centre, one of the best IVF centres in Delhi, says that in men, a lack of glucose in particular parts of the brain can lead to weariness, weakness, and decreased sexual drive.
Effect of type 1 diabetes in male fertility
Sperm DNA damage: Diabetes is associated with increased mitochondrial, nuclear, and DNA damage in sperm, limiting men’s reproductive capabilities.
Effect of type 2 diabetes in male fertility
Quality of sperm: Type 2 diabetes is linked to low sperm count and poor movement. Structural injury to the DNA of the sperm has also been observed.
How is diabetes-related infertility treated?
Diabetes treatment for infertility entails enhanced glycemic control (management of blood sugars), effective control over reproductive hormones, and functionality in men and women. Infertility is frequently diagnosed and treated by looking at the couple’s medical and family histories together.
While adopting healthy adjustments before getting pregnant can add time to the process, it does not have to be a major setback!
According to Dr. Hrishikesh Pai, a top-notch IVF doctor in Delhi, being proactive and making a few simple lifestyle adjustments will help you move forward with your desire to become parents.
Lifestyle changes your health professional may recommend:

Moderate physical activity 5 times a week
Changing your diet is a good idea (decrease simple sugars and increase fiber, complex carbs, lean protein, and veggies)
If you are overweight, then reduce your body weight by 5%-10%
It is often more beneficial for you and your partner to work together in this journey. With a dedication to reach your goals together, you can lower your glucose levels in 2-3 months and move ahead with your aim of having a child.
The following are some of the medical treatment options:
Medications: In addition to treating infections, medications are frequently used to promote ovulation in women.
In men, premature ejaculation and erectile dysfunction (ED) are also treated with medications (sometimes in combination with hormone supplements).
Surgical intervention: Surgical management is frequently required to address uterine fibroids, PCOS, trauma injuries, and other conditions.
ART (Advanced reproductive technologies): ART specialists employ sperm retrieval and ICSI (intracytoplasmic sperm injection) operations for men.
IVF (in-vitro fertilization), IUI (intrauterine insemination), and aided laser hatching are the most common procedures used by women.
Conclusion

Preconception is an excellent time to review your lifestyle and start making the required changes to ensure your best health. Making the changes now will create a healthy and powerful environment for implantation and fetal growth.
The goal is to keep your blood sugar levels in a healthy range so that you can get pregnant and carry it to full-term. It is all about cutting your risks, keeping track of your weight, eating well, and diligently following your doctor’s advice. It may be necessary to seek the assistance of a fertility expert at times.
Please do not delay any longer; schedule an appointment with Dr. Hrishikesh Pai, among the most preferred IVF specialists in Delhi, for his advice and expertise to guide you in the best possible way forward.
Everyone wants a successful pregnancy, healthy parents, and a healthy child, and Dr. Hrishikesh Pai is here to help you get there safely and effectively.

